In the world of fleet management, the ability to collect, transmit, and interpret data from your vehicles is crucial. Teltonika, a leader in telematics solutions, offers various codecs to ensure efficient and accurate data transmission. Understanding these codecs and their differences can help you optimize your fleet management operations and choose the right one for you. In this post, we’ll explore Teltonika telematics codecs and explain why Codec 8e stands out as the most advanced protocol for data sending.
What is a Codec?
A codec (short for coder-decoder) is a protocol that encodes data for transmission and decodes it upon receipt. In the context of telematics, codecs define how information from vehicle tracking devices is formatted and sent to your fleet management system. The choice of codec affects the efficiency, detail, and reliability of the data you receive.
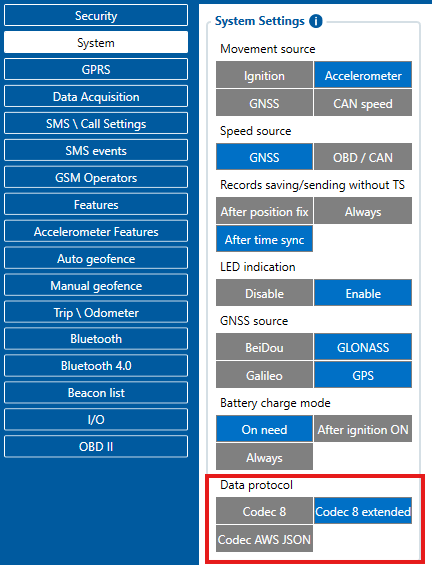
In Teltonika Configurator you can select devices codec in the System -> Data protocol field.
Overview of Teltonika Codecs
Teltonika offers several codecs, each designed to meet different data transmission needs:
- Codec 8. The standard binary protocol for encoding a wide range of telematics data. It’s efficient and reliable, making it a popular choice for basic fleet management needs. As trackers provided users with more and more information, technical limitations were reached which required to improve this protocol, thus Codec 8E superseeded it..
- Codec 8 Extended (8E).: An enhanced version of Codec 8, providing additional data fields and more detailed information. Codec 8E protocol ads an additional byte for avl-id decoding (which in theory allows to send 65535 different IO elements instead of 255 in Codec 8) and introduces a new N-x element type which allows to send variable length IO elements (such as crash traces).
- Codec 12. The standard protocol used for GPRS messages. It does not replace regular codecs (like 8/8E/16) used for data transmissions but extends them
- Codec 16. Designed for specialized data transmission, but often used by the legacy systems. Codec 16 offered wider number of AVL IDs than Codec 8, but got superseded by Codec 8E. Due to the fact, that Codec16 is used only for FMB630/FM63XY devices, there are no benefits in using this protocol over Codec 8E.
- Codec JSON. This codec encodes data in JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) format, which is widely used in web technologies. JSON’s human-readable structure makes it easy to integrate with various software platforms and cloud-based services, making it ideal for modern web-based fleet management systems.
So why Teltonika Telematics Codec 8E and not Codec JSON?
Even though Codec JSON is more human readable, it is not optimal for IoT devices. Codec8E encodes data into the proprietary binary protocol which does not waste any unnecessary bites. This means, that packets are sent faster, more efficiently and thus – end users experience lower SIM card network usage.
For most of the cases we recommend using Codec 8E, due to the following advantages:
- Enhanced Data Fields. Codec 8e includes a variaty of different size data fields. This means you can capture more information about your vehicles’ performance and status, leading to better insights and decision-making.
- Greater Efficiency. Despite the increased amount of data, Codec 8e is designed to be efficient in terms of data size and transmission speed. This means you get more information without compromising on the speed and efficiency of data transfer.
- Advanced Features. Codec 8e supports advanced features such as variable length IO elements. This allows trackers to send data, that would not fit into the standard 1,2,4 or 8byte data models.
- Compatibility and Flexibility. While Codec JSON is flexible and ideal for integration with web applications, Codec 8e is optimized specifically for telematics data, making it the best choice for vehicle tracking and fleet management.
- Future-Proofing. As telematics technology evolves, Codec 8e is designed to accommodate future enhancements and additional data requirements. This makes it a future-proof choice, ensuring that your fleet management system remains compatible with upcoming advancements in telematics. Codec 8E has a lot of room for additional IO ids and can handle edge cases when necessary data packet exceeds 8bytes.
Conclusion
Choosing the right Teltonika Telematics Codec for your fleet management solution can significantly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of your operations. While Teltonika offers several codecs to meet different needs, Codec 8e emerges as the most modern and comprehensive option.
By adopting Codec 8E, you can ensure that your trackers always send data in the most efficient way and utilize all the latest improvements, that firmware updates bring. Fliteca will always be ready to improve and adapt their decoders to utilize those newly added features!
If you have any additional questions, don’t hesitate to contact us!
Happy Tracking!
-Fliteca Team